Labels
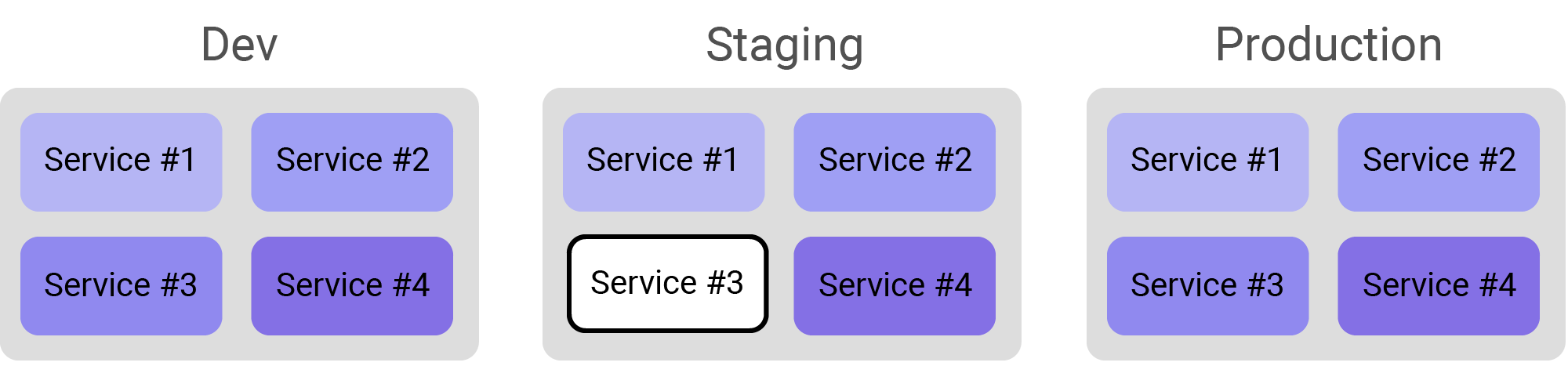
Labels are key/value pairs that are attached to running application instances.
Labels can be used to organize and select groups of application instances. In this example organization, there are three environments - development, staging, and production with 4 different services in each environment.
Setting up your Rookout deployment
When installing the Rookout SDK, you may provide the service name and environment name as labels. For example, service #3 in Production may be configured using the following:
- Python
- Node
- JVM
- .NET
rook.start(token='[Your Rookout Token]',
labels={"service":"service#3","env":"dev"})
rook.start({
token: '[Your Rookout Token]',
labels:
{
"service":"service#3",
"env":"dev"
}
});
# Export your labels as an environment variable
export ROOKOUT_LABELS=service:service3,env:dev
Rook.RookOptions options = new Rook.RookOptions()
{
token = "[Your Rookout Token]",
labels = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "service", "service#3" }, { "env", "dev" } }
};
Rook.API.Start(options);
Altenatively, labels can be added as environment variables in Python and Node as well:
export ROOKOUT_LABELS='service:service3,env:dev'
Examples
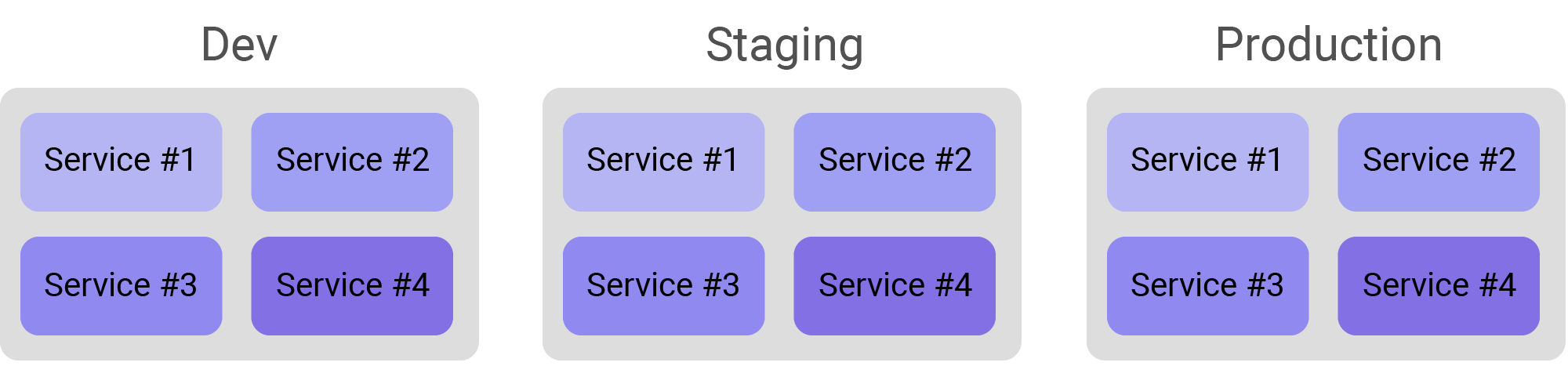
Debug all instances of specific service
When creating your Rookout Project, use the following filter to debug all instances of service #3 (in Production, Staging and Dev).
-
Add the following filter:
service:service#3 -
Import the source code for service #3.
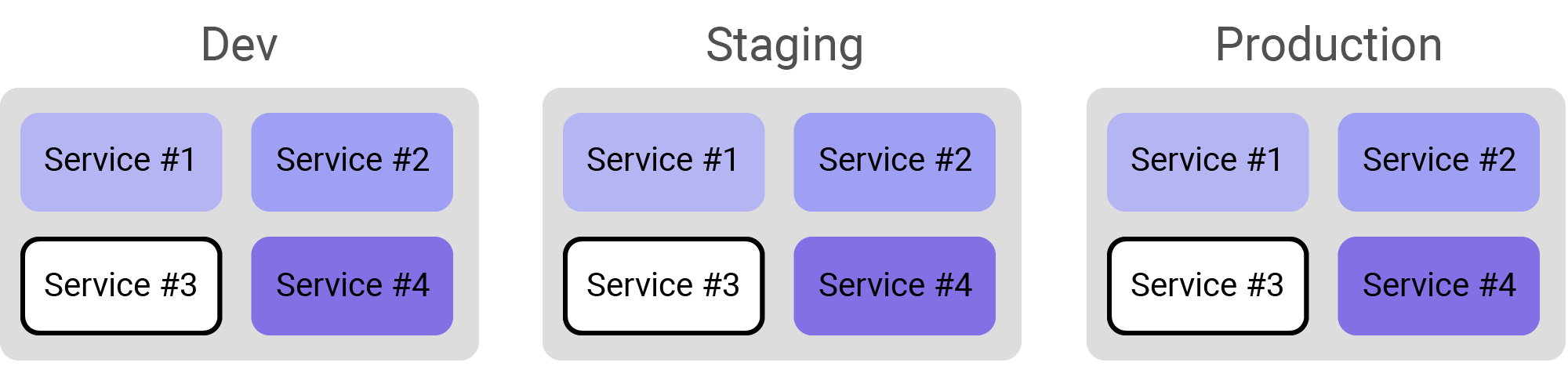
Debug all instances in specific environment
When creating your Rookout Project, use the following filter to debug only instances running in Production.
-
Add the following filter:
env:production -
Import the source code of the relevant service.
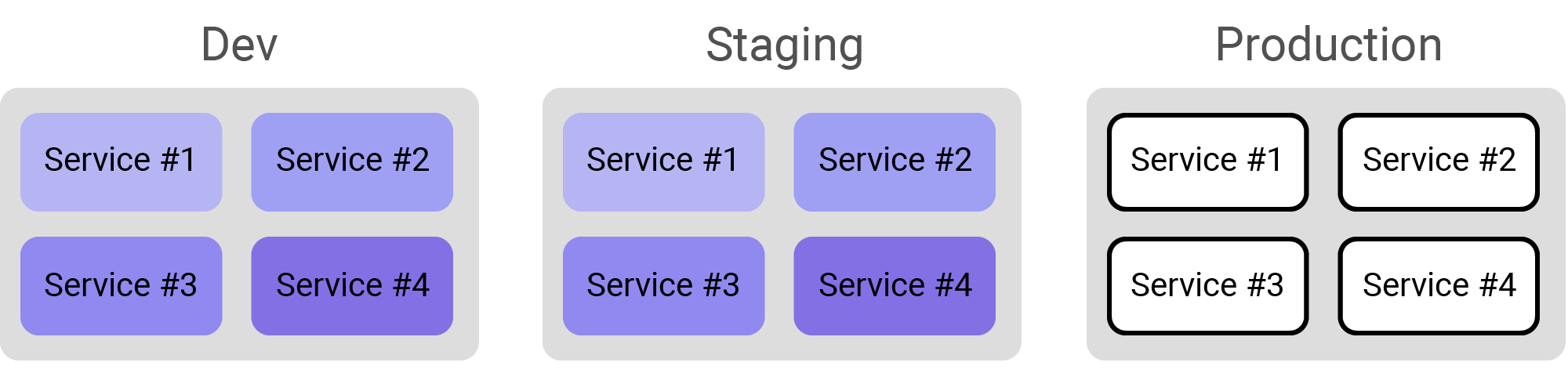
Debug specific instance in specific enviroment
To refine the filter, you may use the following filter to debug only the instance of service #3 running in Staging.
-
Add the following filters:
env:stagingservice:service#3 -
Import the source code for service #3.